EtherChannel or Port-Channel or Eth-Trunk is a link aggregation technology in which multiple physical port links are grouped into one logical link to provide-
- Redundant Links
- Higher Bandwidth by sharing traffic on all links
- Loop solving solution between switches while connecting multiple links
Today, we will do deep drive in EtherChannel. Let’s get Started with EtherChannels which is sometimes refered as port-channel or LAG (link aggregation) or Eth-Trunk.
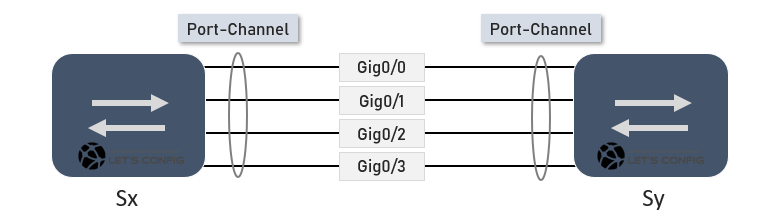
EtherChannel Types
There are two types of link aggregation protocols. These are-
- Static Link Aggregation
- Dynamic Link Aggregation
Static Link Aggregation
This is manual link aggregation, where multiple links will be aggregated into one to provide higher interface throughput and redundancy. This is mainly configured where dynamic is not supported or topology rarely changes.
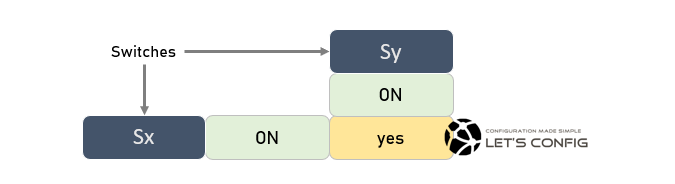
Configuration is very simple for Static Link Aggregation. The only condition is, both switches must need to enable mode “ON”. Any other combination will not work.
Sx Switch
Sx(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode on
Sy Switch
Sy(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode onDynamic Link Aggregation
Dynamic Link Aggregation is a method to automatically bundle multiple physical links into a single logical link. Similar to static link aggregation, it increases higher bandwidth and better redundancy.
Dynamic link aggregation is divided into two categories.
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP)
What is LACP?
LACP is IEEE 802.3ad standard, that means it’s open and it can be configured in any OEM like Cisco, Juniper, Huawei. We can create with maximum 16 links, with 8 will be in active state and remaining 8 links in standbay.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) works in two (2) modes. These are –
- Active Mode
- Passive Mode
SWITCH(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode ?
active Enable LACP unconditionally
passive Enable LACP only if a LACP device is detected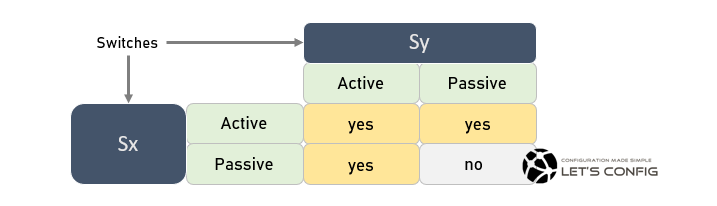
Understanding LACP Active Mode
In this mode, the network device sends LACP packets to it’s peer device to form port-channel. Consequently, peer end can configure either Active or Passive.
Active/Active
Sx Switch
Sx(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode active
Sy Switch
Sy(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode activeActive/Passive
Sx Switch
Sx(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode active
Sy Switch
Sy(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode passiveUnderstanding LACP Passive Mode
Here, network device doesn’t transmit any LACP packets, but instead wait to receive LACP packets from peer node. That means. the other node must be LACP active to establish LACP between two nodes.
Active/Passive
Sx Switch
Sx(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode passive
Sy Switch
Sy(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode activeBut, if you configure Passive/Passive mode, then eth-trunk (port-channel) will not be established. Because, both swtiches will wait to receive LACP neighborship packets which will never be received.
What is PAgP?
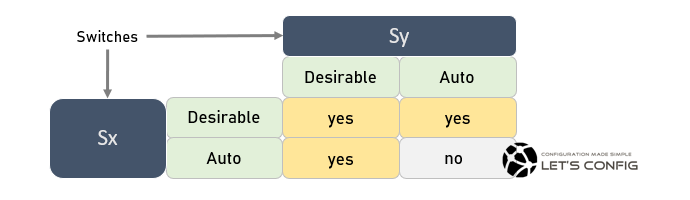
PAgP is Cisco proprietary protocol. It can marge eight (8) links into one virtual link. PAgP works in two (2) modes-
- Desirable Mode
- Auto Mode
Understanding PAgP Desirable Mode
It’s similar to LACP active mode. Here network device actively sends PAgP packets to establish port-channel. Peer end can configure either desirable or auto mode to establish PAgP.
Desirable/Desirable
Sx Switch
Sx(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirable
Sy Switch
Sy(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirableDesirable/Auto
Sx Switch
Sx(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirable
Sy Switch
Sy(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode autoUnderstanding PAgP Auto Mode
In this mode, node don’t send any PAgP packets, but it’s wait for PAgP packets. If it received any packets from desirable enabled node, it will establish. Below are the plan you need to follow to form PAgP peer.
Desirable/Auto
Sx Switch
Sx(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode auto
Sy Switch
Sy(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode desirableUpcoming post on EtherChannel
- How to configure EtherChannel in Cisco
- Understanding LACP load-balancing mechanism
- Troubleshooting Port Channels
If you have any questions on link aggregation, feel free to ask.


Hello,
Do all ports added to an EtherChannel group need to have the same speed for the configuration to work properly?
For some OEM it’s mendatory, for some it’s not.