Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol to collect and organize information about device in an IP network. In this lesson, we will learn to configure SNMP v2c in Cisco device.

Pre-Check:
Make sure port 161 is open for SNMP pulling from the device. And, also 162 need to be open to send trap from device to snmp server.
Configuration of SNMP in Cisco:
Enabling the SNMP v2c in Cisco IOS devices are easy. You just need to run below commands-
snmp-server community letsconfigRO RO snmp-server community letsconfigRW RW
Explanation:
letsconfigRO is the community-string for read-only.
letsconfigRW is the community-sting for read-write.
SNMP Trap
If you want to send notification from device to SNMP server, then you need to enable trap and specify the SNMP host server.
snmp-server host 192.168.2.181 version 2c letsconfigRO snmp-server enable traps
Explanation:
192.168.2.181 is the SNMP server address.
version 2c is the SNMP version.
letsconfigRO is the community-sting for SNMP trap.
snmp-server enable traps commands enables trap for all the notification. If you want, you can enable trap for particular incident as per your requirements.
Example:
LetsConfig-RTR(config)#snmp-server enable traps ? aaa_server Enable SNMP AAA Server traps atm Enable SNMP atm traps auth-framework Enable SNMP CISCO-AUTH-FRAMEWORK-MIB traps bfd Allow SNMP BFD traps bgp Enable BGP traps bstun Enable SNMP BSTUN traps bulkstat Enable Data-Collection-MIB Collection notifications cef Enable SNMP CEF traps cnpd Enable NBAR Protocol Discovery traps config Enable SNMP config traps config-copy Enable SNMP config-copy traps config-ctid Enable SNMP config-ctid traps cpu Allow cpu related traps diameter Allow Diameter related traps dlsw Enable SNMP dlsw traps dsp Enable SNMP dsp traps eigrp Enable SNMP EIGRP traps entity Enable SNMP entity traps entity-ext Enable SNMP entity extension traps ethernet Enable SNMP Ethernet traps event-manager Enable SNMP Embedded Event Manager traps firewall Enable SNMP Firewall traps --More-- LetsConfig-RTR(config)# snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkdown linkup coldstart warmstart
Here is the final configuration.
snmp-server community letsconfigRO RO snmp-server community letsconfigRW RW snmp-server enable traps snmp authentication linkdown linkup coldstart warmstart snmp-server host 192.168.2.181 version 2c letsconfigRO
Verification
First of all, run show snmp from the device.
LetsConfig-RTR#show snmp
10 SNMP packets input
0 Bad SNMP version errors
4 Unknown community name
0 Illegal operation for community name supplied
0 Encoding errors
6 Number of requested variables
0 Number of altered variables
6 Get-request PDUs
0 Get-next PDUs
0 Set-request PDUs
0 Input queue packet drops (Maximum queue size 1000)
16 SNMP packets output
0 Too big errors (Maximum packet size 1500)
0 No such name errors
0 Bad values errors
0 General errors
6 Response PDUs
10 Trap PDUs
SNMP Dispatcher:
queue 0/75 (current/max), 0 dropped
SNMP Engine:
queue 0/1000 (current/max), 0 dropped
SNMP logging: enabled
Logging to 192.168.2.181.162, 0/10, 10 sent, 0 dropped.
Secondly, you can check from SNMP server. I will recommend lightweight free application named SnmpB. You can download and install SnmpB from sourceforge.
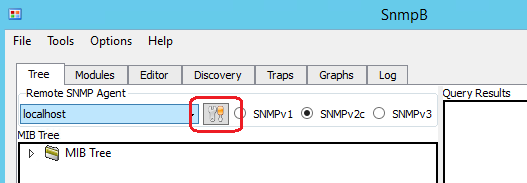
After install, open the application and go to EDIT as per below diagram.
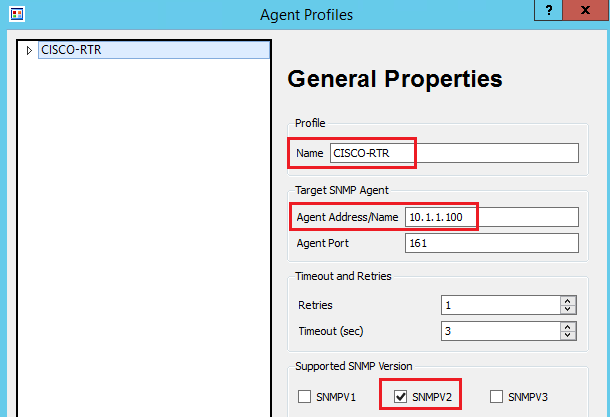
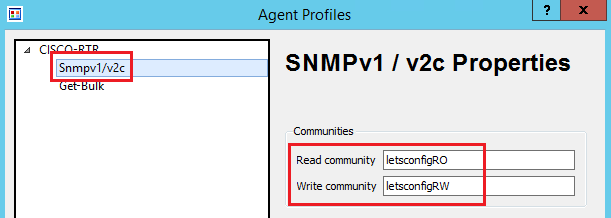
Now, add all the details, including the community string.
SNMP server setup is done. Let’s pull some information of the device. Following steps to pull device hostname. You can pull other information as well.
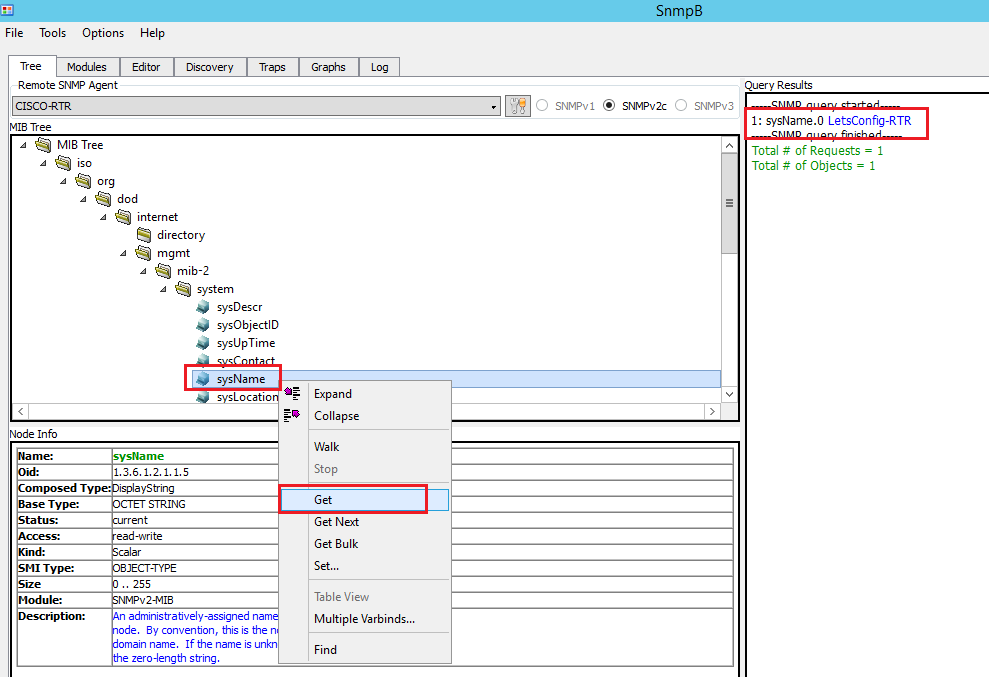
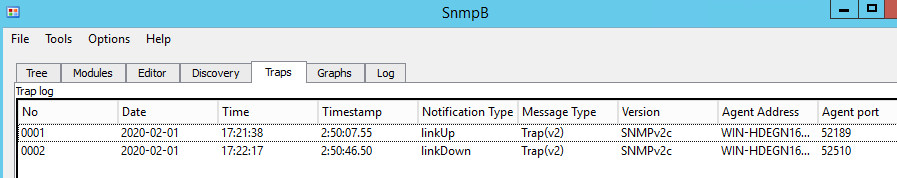
We also can check SNMP trap information. Just go Trap and see the information. You can bounce your interface to see the output (just run shutdown and no shutdown command) to generate trap information.